cooling tower parts & Functions
35000.0 INR/Number
தயாரிப்பு விவரங்கள்:
- பயன்பாடு industrial
- பொருள்
- தயாரிப்பு வகை cooling tower parts & Functions
- விண்ணப்பம் cooling tower
- உத்தரவாதத்தை yes
- மேலும் பார்க்க கிளிக் செய்யவும்
X
விலை மற்றும் அளவு
- 100
தயாரிப்பு விவரக்குறிப்புகள்
- cooling tower
- cooling tower parts & Functions
- yes
- industrial
வர்த்தகத் தகவல்கள்
- மாதத்திற்கு
- வாரம்
தயாரிப்பு விளக்கம்
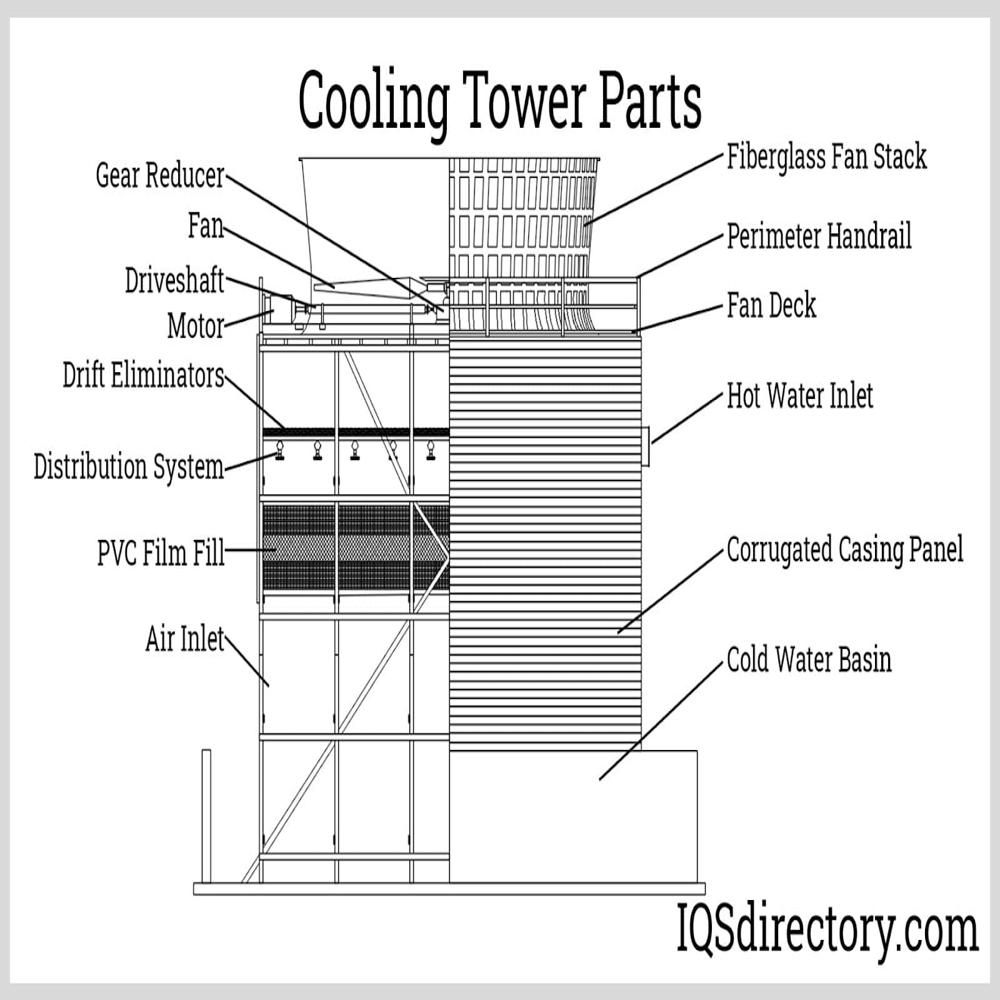
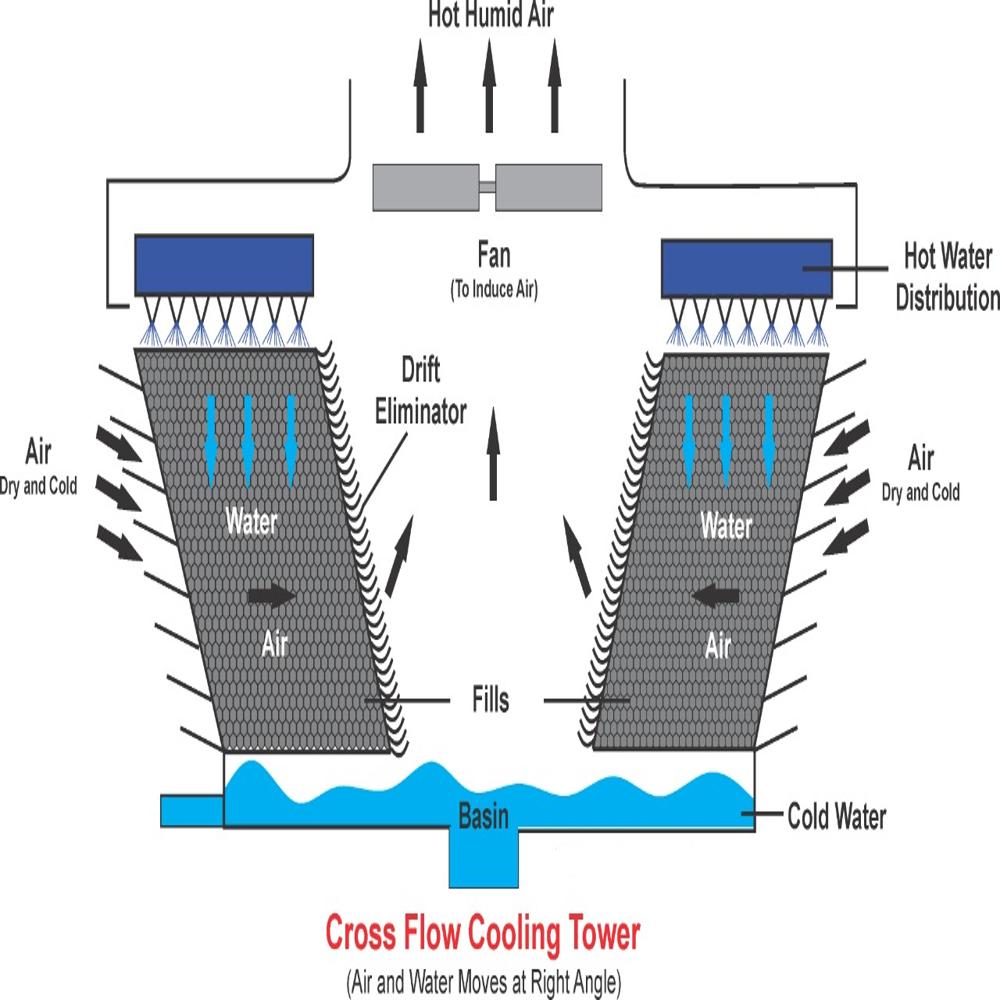
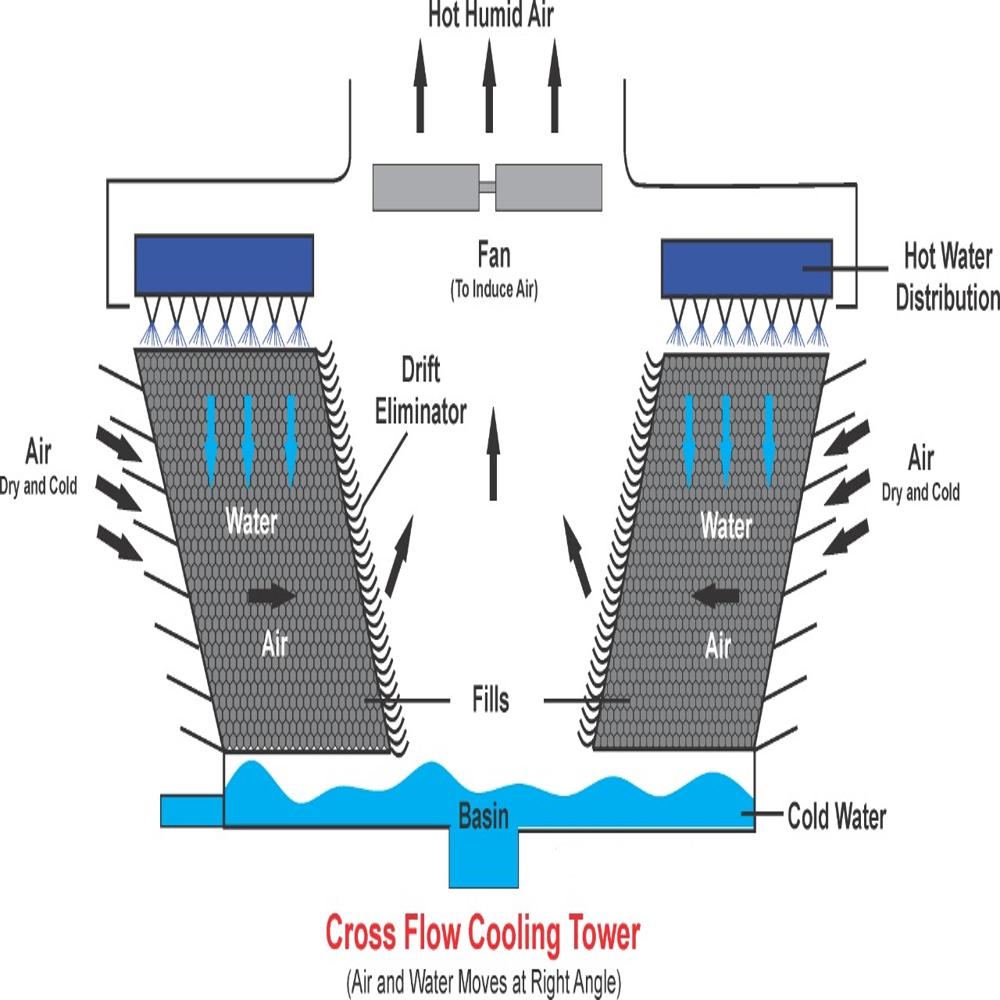
Cooling towers, essential for heat dissipation, consist of key parts likebasins, fills, nozzles, and drift eliminators, each playing a crucial role in the cooling process, and can vary significantly in size and shape.
Key Parts and Functions:
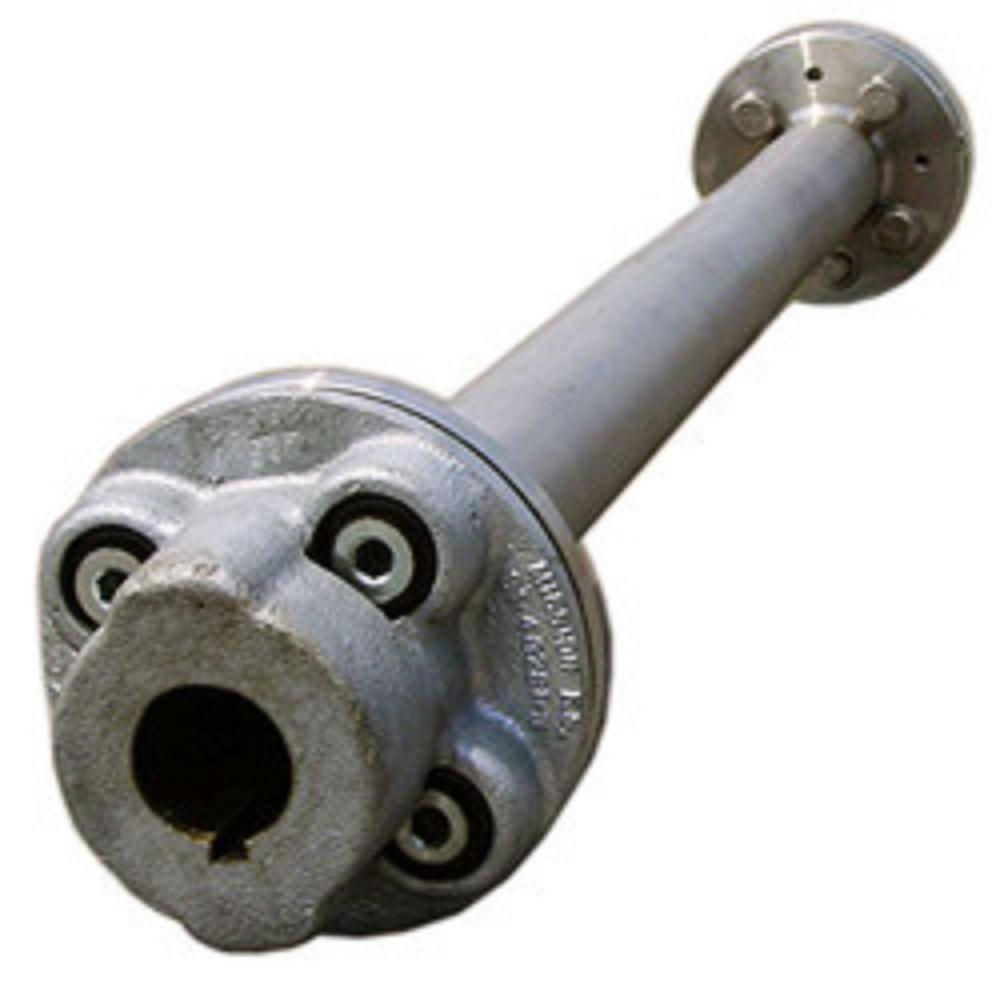
- Cooling Tower Basin:
- Collection Basin:Located at the bottom, it collects cooled water and directs it to the pump suction line or sump.
- Distribution Basin:An elevated, shallow-type basin that distributes hot water to the tower via holes in the basin floor.
- Cold Water Basin:Serves as storage for cold water and provides the main structure and foundation for the cooling tower.
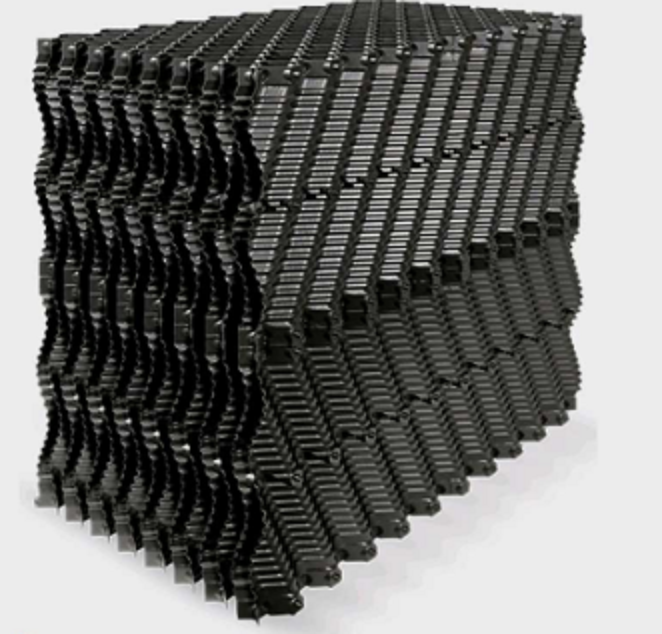
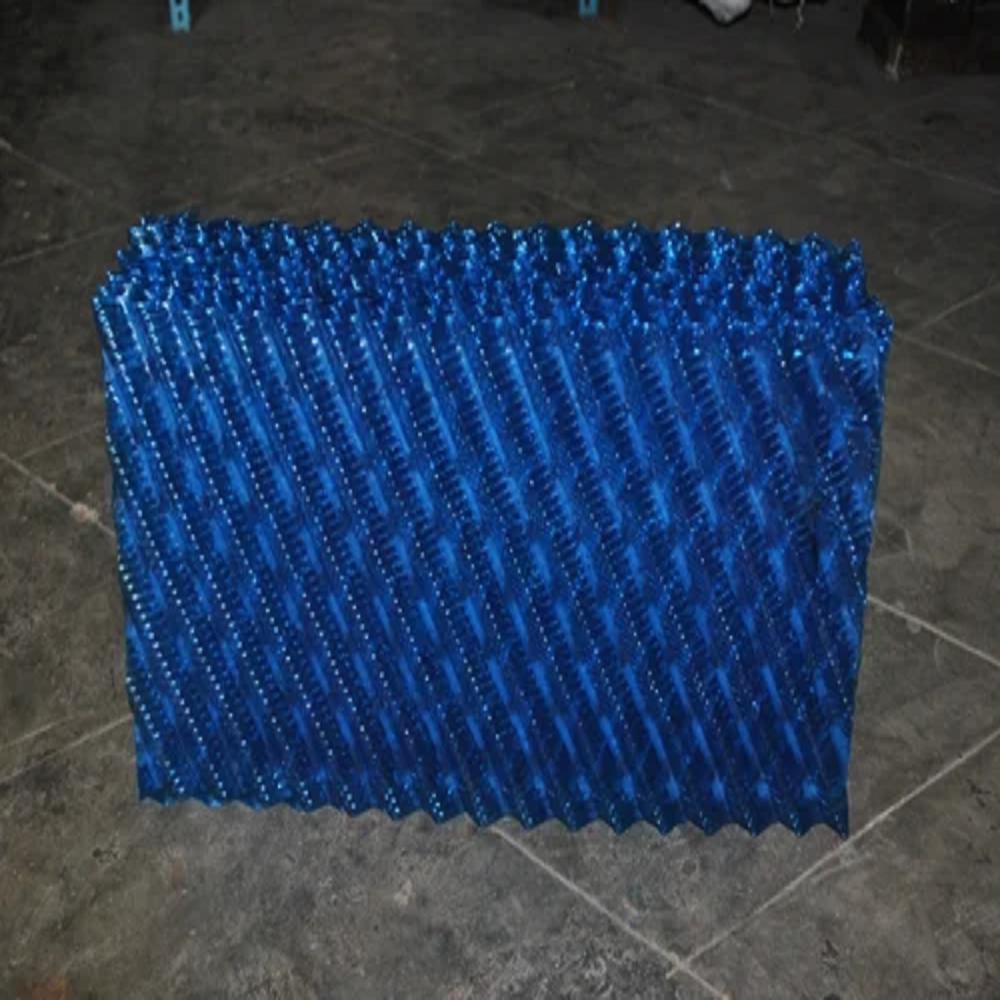
- Cooling Tower Fills (Heat Exchange Surface):
- These are the surfaces where water and air interact, facilitating heat exchange.
- They are designed to maximize contact between air and water for efficient heat dissipation.
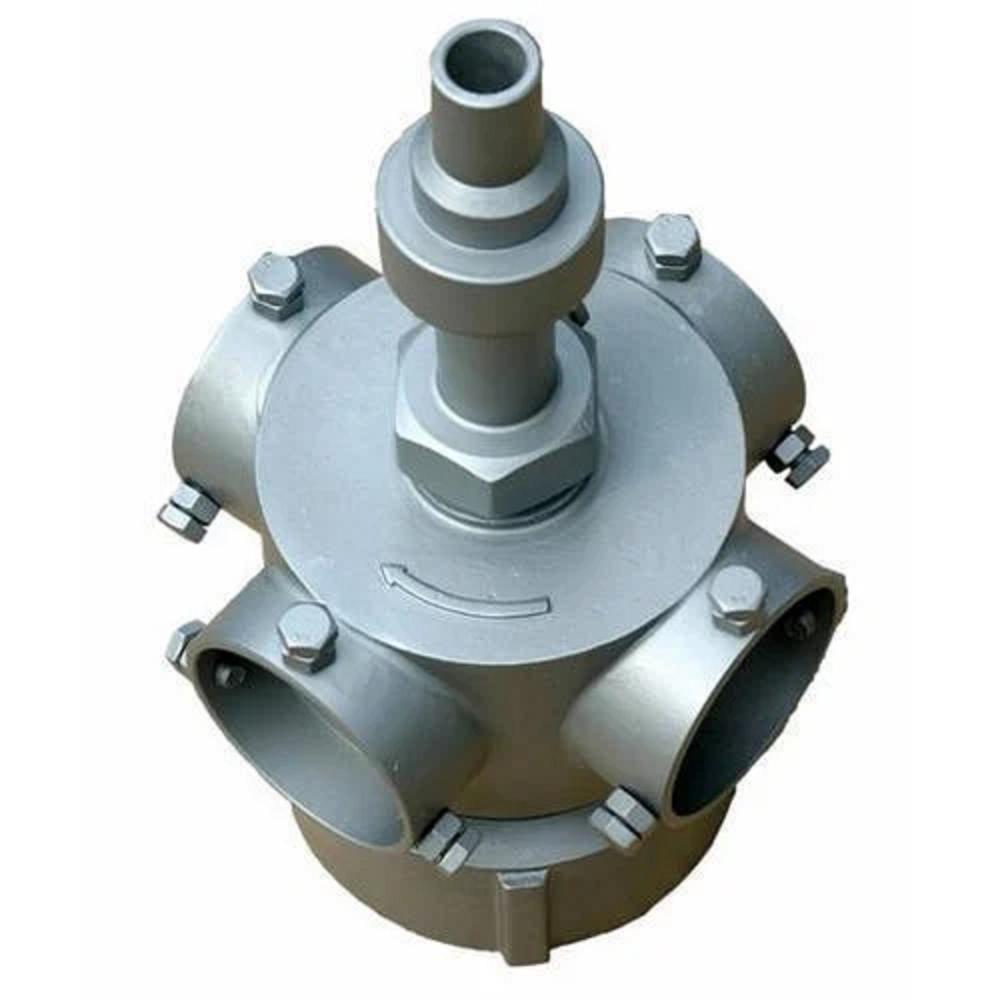
- Cooling Tower Nozzles:
- These are affixed to the hot water pipes and spray water onto the fills.
- They contribute to the enhancement of the cooling effect by dispersing water across a broad area.
- Cooling Tower Drift Eliminator:
- These capture large water droplets from the air stream, preventing them from being carried away.
- Other Important Parts:
- Fans:Driven by motors, they circulate air through the tower to promote evaporation and heat transfer.
- Gearbox:Slows down the rotational speed from the motor to the fan.
- Driveshafts:Connect the motor and gearbox, transmitting power.
- Air Intake Louver:Blocks water splash-out, noise, and debris.
- Piping:Distributes water within the cooling tower.
- Float Valve:Maintains the right water levels inside the cooling tower.
Length and Width:
- Cooling towers come in various sizes, from small roof-top units to large hyperboloid structures.
- Hyperboloid towers can be up to 200 meters (660 ft) tall and 100 meters (330 ft) in diameter.
- Rectangular structures can be over 40 meters (130 ft) tall and 80 meters (260 ft) long.
- A cooling tower example is 21.65 m wide 36.9 m long 15.24m high.
Tell us about your requirement

Price: Â
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
கைபேசி number
Email