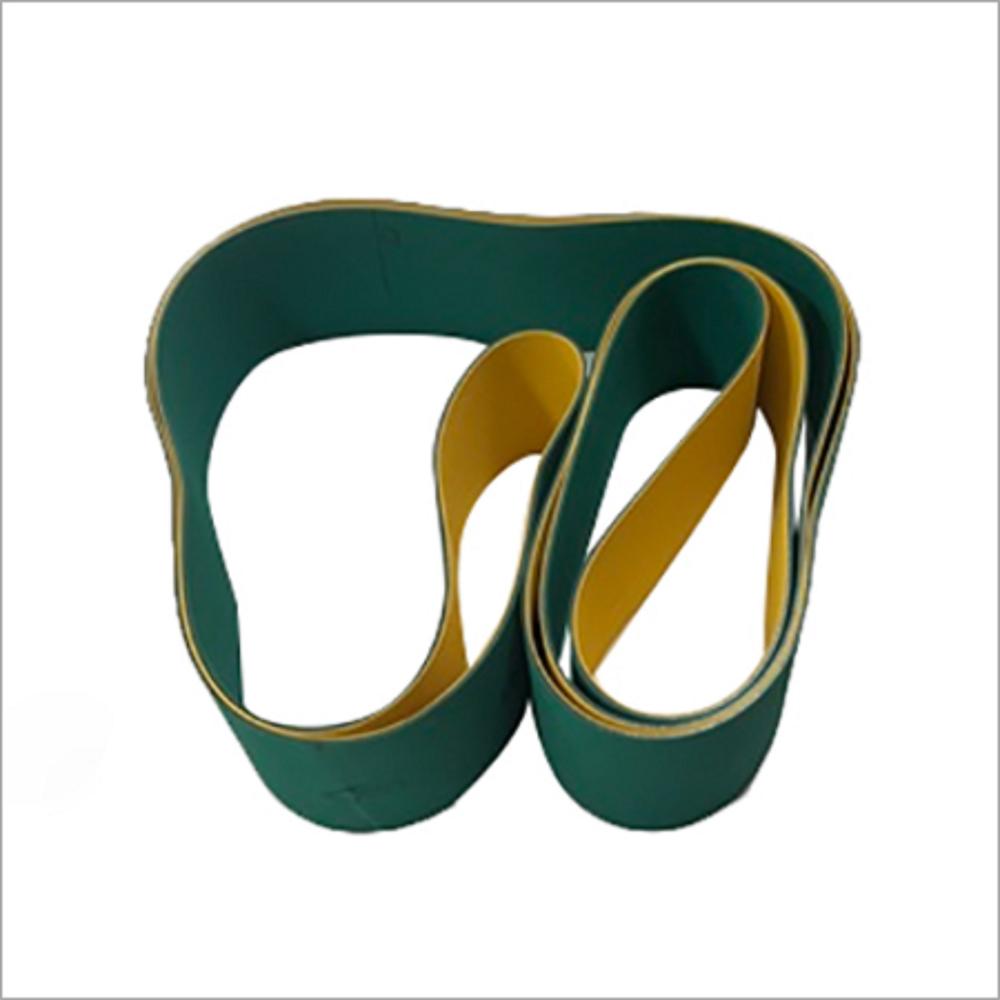
Cooling tower Fan Belts
தயாரிப்பு விவரங்கள்:
- விண்ணப்பம் COMMERCIAL
- பொருள்
- கலர் GREEN
- கண்டிஷன்
- உத்தரவாதத்தை YES
- மேலும் பார்க்க கிளிக் செய்யவும்
விலை மற்றும் அளவு
- 1
தயாரிப்பு விவரக்குறிப்புகள்
- YES
- GREEN
- COMMERCIAL
வர்த்தகத் தகவல்கள்
- மாதத்திற்கு
- வாரம்
தயாரிப்பு விளக்கம்
In a belt-driven cooling tower system,the motor's power is transmitted to the fan shaft via a belt, which is attached to a sheave on the fan shaft, with bearings and bushings holding everything together.This system offers smooth and effective power transmission, even over distances, requiring regular belt lubrication and tensioning for optimal performance.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
- Power Transmission:
The motor and its sheave (pulley) provide the power, which is then transferred via the belt to the fan shaft's sheave.
- Sheave Alignment:
Proper alignment between the motor and fan sheaves is crucial for efficient and reliable operation.
- Bearing and Bushing:
Bearings and bushings support the sheave and ensure smooth rotation of the fan shaft.
- Maintenance:
Regular maintenance, including belt lubrication, tensioning, and sheave alignment checks, is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the belt-driven system.
- Belt Types:
V-belts are commonly used in cooling tower fan drive systems.
- Belt Drive Systems:
Belt drive systems are cost-effective and reliable, particularly for motors up to 75 HP.
- Fan Speed:
The fan speed is determined by the motor speed and the ratio of the motor and fan sheave diameters.
- Maintenance Procedures:
Routine drive maintenance procedures include belt tension checks and fan shaft bearing lubrication.
- Variable Frequency Drives:
Using variable frequency drives can extend belt life and provide soft start capabilities.
- Belt Life:
Belts are considered "wear" items and may need replacement periodically, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Cooling Tower Function:
Cooling towers are used to reject heat into the atmosphere by cooling water that has been heated by industrial processes.
- Fan Role:
Fans play a critical role in the air circulation within the cooling tower, either pulling air up through the tower (induced draft) or pushing air into the tower (forced draft).
- Induced Draft Systems:
Induced draft systems use fans at the top of the tower to pull air through, while forced draft systems use fans at the air intake louvers to push air into the tower.

Price: Â
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+